The .NET Runtime Optimization Service is a process that precompiles .NET assemblies in the background. This operation improves the performance of .NET applications on your computer. Normally, this process completes quickly and doesn't impact your system resources. However, sometimes it consumes a lot of CPU and slows down your PC. In this article, we'll explain the possible causes of this problem and how to easily resolve it.
The causes of the problem

There are several reasons why the .NET Runtime Optimization Service might be using a lot of CPU on your computer. Here are the most common ones:
- The process is running slowly and taking longer than expected to precompile the .NET assemblies.
- Your computer is infected with malware that interferes with the process or hijacks it for malicious purposes.
- The service is damaged or corrupted and is not functioning properly.
- You have installed or updated applications that use the .NET Framework and require a new precompilation of assemblies.
Possible solutions
Fortunately, there are several solutions you can try to resolve the issue of high CPU usage by the .NET Runtime Optimization Service. We'll present the most effective and easiest to implement.
Solution 1: Speed up the process
The first thing you can do is try to speed up the .NET assembly precompilation process by allocating more CPU resources . To do this, you need to run a command in the command prompt as an administrator. Here are the steps:
- Press the Windows + R Run dialog box .
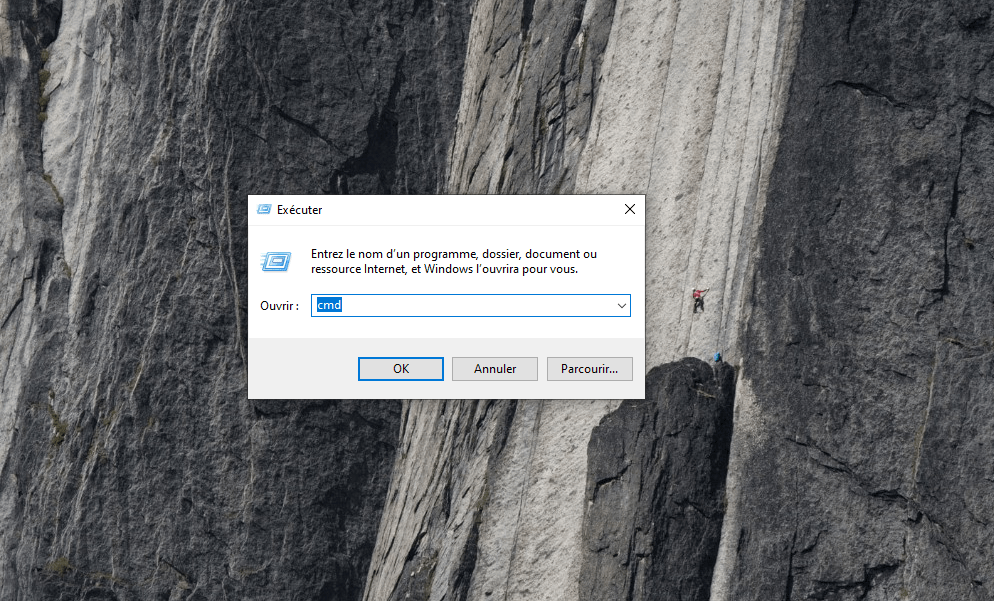
- Type cmd and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open the command prompt as an administrator.
- Copy and paste the following commands into the command prompt and press Enter after each one:
cd C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319 ngen.exe executequeueditems cd C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319 ngen.exe executequeueditems
- These commands will force the NET Runtime Optimization Service to complete its task faster by using all available cores of your processor.
- Wait for the process to finish and check if the problem is resolved.
Solution 2: Scan for malware
Another possible cause of the problem is the presence of malware on your computer that can interfere with the operation of the .NET Runtime Optimization Service or use it for malicious purposes. To eliminate this possibility, you should perform a full system scan with reliable and up-to-date antivirus software . You can use the built-in Windows 10 antivirus, Windows Defender , or another antivirus program of your choice. Here's how to perform a scan with Windows Defender:
- Press the Windows + I to open Windows Windows Settings .
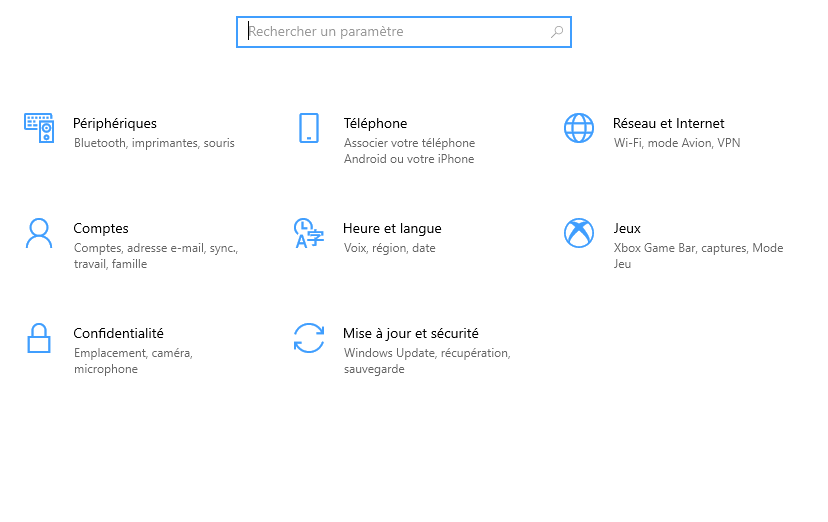
- Click on Update & Security , then on Windows Security in the left menu.
- Click on Virus & threat protection , then on Scan options .
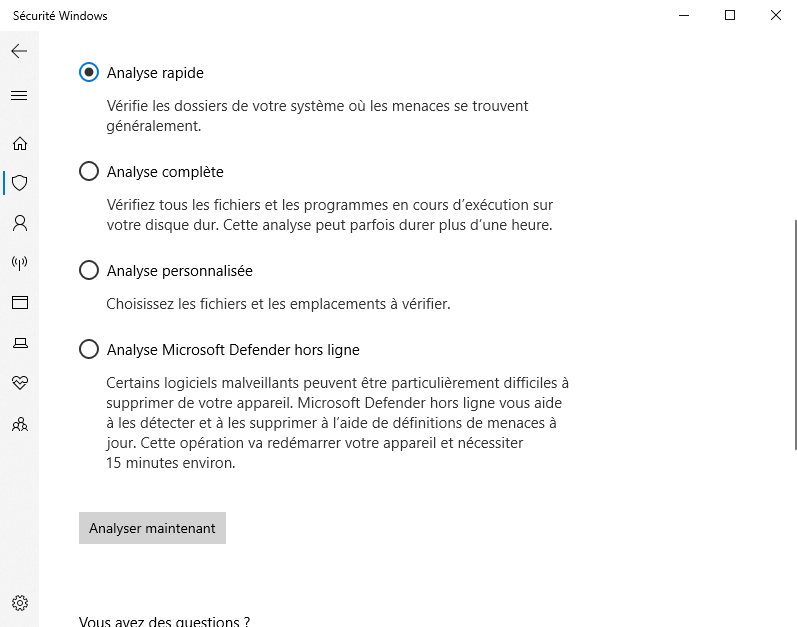
- Select Full Analysis and click Analyze Now.
- Wait for the scan to finish and follow the on-screen instructions to remove any detected threats.
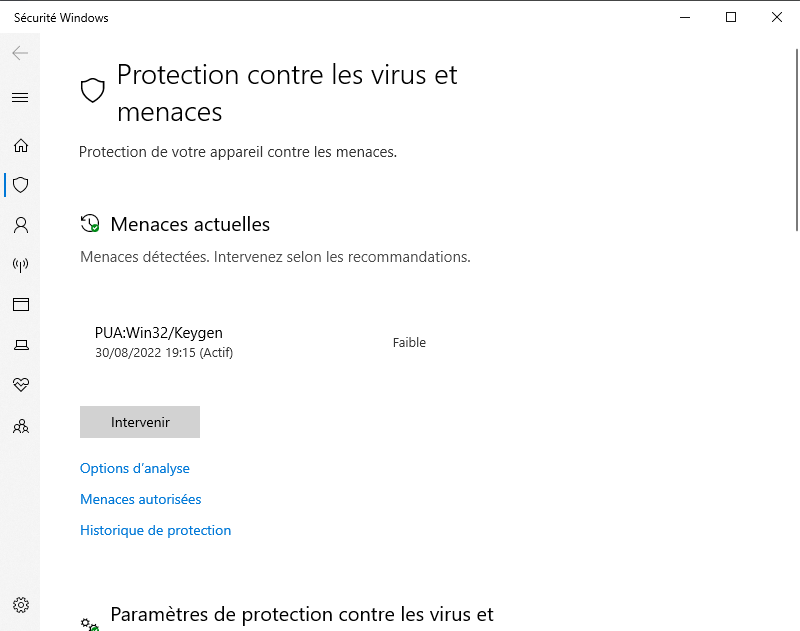
- Restart your computer and check if the problem is resolved.
Solution 3: Restart the services
Another possible solution is to restart the services related to the .NET Runtime Optimization Service. These services may be blocked or not functioning correctly. To restart them, you need to use the WindowsServices Manager. Here's how:
- Press the Windows + R Run dialog box .
- Type services.msc and click OK to open the Services Manager.
- Search for the following services in the list:
- Microsoft .NET Framework NGEN v4.0.30319_X86
- Microsoft .NET Framework NGEN v4.0.30319_X64
- Microsoft .NET Framework NGEN v2.0.50727_X86
- Microsoft .NET Framework NGEN v2.0.50727_X64
- Right-click on each service and select Restart .
- Wait for the services to restart and check if the problem is resolved.
Solution 4: Disable the service
If none of the previous solutions work, you can try disabling the .NET Runtime Optimization Service . This solution is not recommended, as it can affect the performance of .NET applications on your computer. However, if you don't use these applications often or are willing to sacrifice some speed to reduce CPU usage, you can try this solution. Here's how:
- Press the Windows + R Run dialog box .
- Type services.msc and click OK to open the Services Manager.
- Microsoft .NET Framework NGEN v4.0.30319_X86 service in the list.

- Right-click on the service and select Properties .
- In the General , change the startup type to Disabled and click OK .
- Repeat the same steps for the other services related to the NET Runtime Optimization Service (see solution 3).
- Restart your computer and check if the problem is resolved.
FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions from users regarding the NET Runtime Optimization Service.
What is the NET Runtime Optimization Service?
The NET Runtime Optimization Service is a process that precompiles .NET assemblies in the background . This operation improves the performance of .NET applications on your computer by reducing startup time and memory consumption.
Why does the NET Runtime Optimization Service use so much CPU?
The .NET Runtime Optimization Service uses a significant amount of CPU when precompiling .NET assemblies in the background. This process can take more or less time depending on the number of assemblies to be precompiled and your system's available resources. Normally, this process completes quickly and doesn't impact your system's resources. However, sometimes it consumes a lot of CPU and slows down your PC. This can be due to several reasons, as explained in this article.
How can I tell if the NET Runtime Optimization Service is running?
You can check if the .NET Runtime Optimization Service is running by opening the Windows . To do this, press Ctrl + Alt + Delete and click Task Manager . In the Processes , look for the process named mscorsvw.exe . If you see it, the .NET Runtime Optimization Service is running.
Can I stop the NET Runtime Optimization Service?
It is not recommended to stop the .NET Runtime Optimization Service , as this can affect the performance of .NET applications on your computer. If you stop the process, it will automatically resume the next time you restart your computer . The best solution is to let the process finish or try the solutions we have presented in this article.
Is the NET Runtime Optimization Service a virus?
No, the .NET Runtime Optimization Service is not a virus . It's a legitimate process that's part of Microsoft's .NET Framework . However, there is malware that can impersonate the .NET Runtime Optimization Service or use it for malicious purposes. That's why it's important to scan your computer with reliable and up-to-date antivirus software.
Conclusion
The .NET Runtime Optimization Service is a useful process that improves the performance of .NET applications on your computer. However, it can sometimes cause high CPU and slow down your PC. In this article, we've presented four possible solutions to easily resolve this issue. We hope this article has been helpful and that you've successfully resolved the high CPU usage problem caused by the .NET Runtime Optimization Service.




