Visual Basic for Applications ( VBA ) is a programming language that allows you to extend Excel's functionality and automate repetitive tasks. With VBA, you can create macros, forms, custom functions, and interactive applications. In this article, you will learn the basics of VBA in Excel and how to use it to perform simple or complex operations.
How do I access VBA in Excel?
To access VBA in Excel, you need to activate the Developer tab in the ribbon. To do this, follow these steps:
- Click the File button and then click Options.

- In the Excel Options window, click on Customize Ribbon.

- In the list of main tabs, check the Developer box and then click OK.
You will then see the Developer tab appear in the ribbon. This tab contains several tools related to VBA, such as the Visual Basic button, the Record Macro button, and the Insert Control button.


The Visual Basic button opens the Visual Basic Editor (VBE), where you create and modify VBA code. The Record Macro button automatically generates VBA code that replicates the actions you perform in the application. The Insert Control button lets you add interactive elements to your spreadsheet, such as buttons, checkboxes, or drop-down lists.
How do I write VBA code in Excel?
To write VBA code in Excel, you must use the Visual Basic Editor (VBE). To open it, click the Visual Basic button on the Developer tab of the ribbon.
The VBE consists of several windows:

- The Project window displays the hierarchical structure of objects containing VBA code. For example, if you have a workbook named MyWorkbook.xlsm with two sheets named Sheet1 and Sheet2, you will see the objects Sheet1 and Sheet2 appear under MyWorkbook.xlsm, as well as an object named ThisWorkbook.

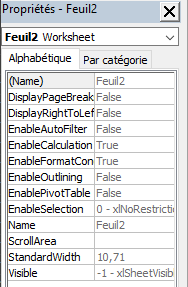
- The Properties window displays the properties of the object selected in the Project window. For example, if you select the Sheet1 object, you will see its properties such as its name (Name), its color (Tab.Color), its code (CodeName), etc.
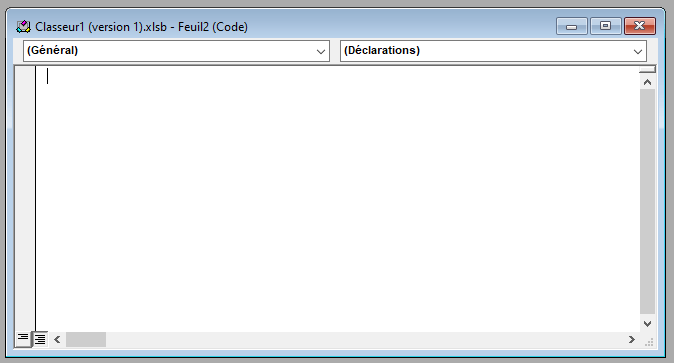
- The Code window displays the VBA code associated with the object selected in the Project window. For example, if you select the Sheet1 object, you will see the VBA code that runs when you interact with the Sheet1 worksheet.
- The Immediate window displays the results of the VBA code or error messages. For example, if you use the MsgBox function to display a message to the user, you will see the message appear in the Immediate window.

To write VBA code, you must follow certain syntax rules:
- Each instruction must end with a line break or a colon character (:).
- VBA language keywords must be written in uppercase or lowercase, but not the names of objects, properties or methods, which are case-sensitive.
- Comments must be preceded by the apostrophe character (') or Rem and must be written on a separate line or after an instruction.
- Strings of characters must be enclosed in double quotes (" ).
- The arithmetic operators are +, -, *, / and ^ (power).
- The logical operators are And, Or, Not, Xor and Eqv.
- The comparison operators are =, <>, <, <=, > and >=.
- The predefined constants are True, False, Null, Empty, Nothing and vbNullString.
Here is an example of VBA code that displays a message to the user:
Sub Hello() ' This is a comment MsgBox "Hello, I'm Bing!" ' Displays a message End SubHow to use Excel spreadsheet functions in VBA?
You can use most Excel spreadsheet functions in your VBA instructions. To do this, you must use the following syntax:
Application.WorksheetFunction.FunctionName(argument1, argument2, ...)For example, if you want to use the SUM function to calculate the sum of the values in the range A1:A10, you can write:
Sub Sum() Dim result As Double ' Declares a variable of type Double result = Application.WorksheetFunction.Sum(Range("A1:A10")) ' Assigns the result of the SUM function to the variable MsgBox result ' Displays the result End SubYou can also use custom functions that you create yourself in VBA. To do this, you must use the following syntax:
Function FunctionName(argument1 As Type1, argument2 As Type2, ...) As ReturnType ' Declarations and instructions FunctionName = expression ' Assigns the result to be returned to the function End FunctionFor example, if you want to create a function that calculates the square of a number, you can write:
Function Square(number As Double) As Double ' Declares a function that takes a number as an argument and returns a number Square = number * number ' Assigns the square of the number to the function End FunctionYou can then use this function in your VBA instructions or in your Excel formulas. For example:
Sub Test() Dim x As Double ' Declares a variable of type Double x = 5 ' Assigns the value 5 to the variable MsgBox Square(x) ' Displays the square of x End SubHow do I create macros in Excel?
A macro is a set of VBA instructions that executes once. You can create macros to automate recurring or complex tasks in Excel. There are two ways to create macros: by recording them or by writing them.
Record a macro
Recording a macro involves using the Record Macro button on the Developer tab of the ribbon to capture the actions you perform in Excel and convert them into VBA code. This is the simplest and fastest way to create a macro, but it can produce poorly optimized or redundant code.
To record a macro, follow these steps:
- Click the Record Macro button in the Developer tab of the ribbon.

- In the Record Macro dialog box, give your macro a name, choose a keyboard shortcut if you wish, select a location to store your macro (active workbook, new workbook, or personal workbook), and write a description if you wish.
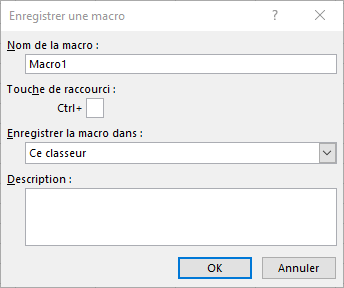
- Click OK to begin recording.
- Perform the actions you want to automate in Excel. For example, if you want to create a macro that formats a table, select the table, apply a style to it, sort it alphabetically, etc.
- Click the Stop Recording button in the Developer tab of the ribbon to end the recording.
You can then run your macro using your chosen keyboard shortcut, by clicking the Macros button in the Developer tab of the ribbon, or by using the Run button in the VBE.
Write a macro
Writing a macro involves using the VBE to directly type the VBA code that corresponds to the actions you want to automate. It's the most flexible and powerful method for creating a macro, but it requires programming knowledge.
To write a macro, follow these steps:
- Open the VBE by clicking the Visual Basic button in the Developer tab of the ribbon.

- In the Project window, select the object where you want to store your macro (active workbook, new workbook, or personal workbook).
- In the Code window, type the VBA code that corresponds to the actions you want to automate. For example, if you want to create a macro that formats a table, type the following code:
Sub FormatTable() ' Selects the table Range("A1:D10").Select ' Applies a style to the table Selection.Style = "Table 1" ' Sorts the table alphabetically by column A ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Sort.SortFields.Clear ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Sort.SortFields.Add Key:=Range("A2:A10") , SortOn:=xlSortOnValues, Order:=xlAscending, DataOption:=xlSortNormal With ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1").Sort .SetRange Range("A1:D10") .Header = xlYes .MatchCase = False .Orientation = xlTopToBottom .SortMethod = xlPinYin .Apply End With End SubYou can then run your macro using the Run button in the VBE or by assigning it a keyboard shortcut or control.

FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about using VBA in Excel:
What is VBA and why use it?
VBA is the version of Visual Basic included with Microsoft Office. It's an object-oriented programming that uses a syntax close to natural language. VBA allows you to access and manipulate Excel's objects, properties, and methods using code. This gives you more precise and powerful control over Excel than through the graphical interface.
Using VBA offers several advantages:
- You can automate repetitive or tedious tasks, such as data cleaning, table formatting, chart creation, etc.
- You can customize Excel to suit your specific needs, adding features that do not exist in the software or modifying its behavior.
- You can interact with the user using dialog boxes, forms, or custom messages.
- You can integrate Excel with other Office applications or external data sources, such as Outlook, Word, Access, SQL Server, etc.
How to debug VBA code in Excel?
To debug VBA code in Excel, you can use VBE tools such as breakpoints, stepping, the Watch window, or the Locales window. These tools allow you to control code execution, check variable values, and spot errors.
How to protect VBA code in Excel?
To protect VBA code in Excel, you can lock the VBA project with a password. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the VBE by clicking the Visual Basic button in the Developer tab of the ribbon.
- In the Project window, right-click on the VBA project name and choose VBA Project Properties.
- In the VBA project properties dialog box, click the Protection tab.
- Check the box to lock the project for viewing and type a password, then confirm it.
- Click OK to close the dialog box.
- Save and close the workbook.
How do I run a macro when opening or closing a workbook?
To run a macro when a workbook is opened or closed, you must use the Workbook_Open or Workbook_BeforeClose events. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the VBE by clicking the Visual Basic button in the Developer tab of the ribbon.
- In the Project window, select the ThisWorkbook object under the workbook name.
- In the Code window, choose Workbook from the Object drop-down list in the upper left corner.
- Choose Open or BeforeClose from the Procedure drop-down list in the top right corner.
- Type the VBA code that calls the macro you want to run. For example:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() ' Executes the macro Bonjour when the workbook is opened Bonjour End Sub Private Sub Workbook_BeforeClose(Cancel As Boolean) ' Executes the macro AuRevoir when the workbook is closed AuRevoir End SubHow to create a form in Excel using VBA?
To create a form in Excel using VBA, you must use the VBA Form Designer. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the VBE by clicking the Visual Basic button in the Developer tab of the ribbon.
- In the Project window, right-click on the VBA project name and choose Insert then UserForm.
- A new UserForm window opens. You can add controls such as labels, text boxes, buttons, etc. by dragging them from the toolbox.
- You can modify the properties of the controls in the Properties window or write VBA code to handle their events in the Code window.
- To display the form, you can use the Show method. For example:
Sub ShowForm() ' Displays the form UserForm1 UserForm1.Show End SubHow to create a custom function in Excel using VBA?
To create a custom function in Excel using VBA, you must use the following syntax:
Function FunctionName(argument1 As Type1, argument2 As Type2, ...) As ReturnType ' Declarations and instructions FunctionName = expression ' Assigns the result to be returned to the function End FunctionFor example, if you want to create a function that calculates the square of a number, you can write:
Function Square(number As Double) As Double ' Declares a function that takes a number as an argument and returns a number Square = number * number ' Assigns the square of the number to the function End FunctionYou can then use this function in your VBA instructions or in your Excel formulas. For example:
Sub Test() Dim x As Double ' Declares a variable of type Double x = 5 ' Assigns the value 5 to the variable MsgBox Square(x) ' Displays the square of x End SubYou can also use custom functions that you create yourself in VBA. To do this, you must use the following syntax:
Function FunctionName(argument1 As Type1, argument2 As Type2, ...) As ReturnType ' Declarations and instructions FunctionName = expression ' Assigns the result to be returned to the function End FunctionFor example, if you want to create a function that calculates the square of a number, you can write:
Function Square(number As Double) As Double ' Declares a function that takes a number as an argument and returns a number Square = number * number ' Assigns the square of the number to the function End FunctionYou can then use this function in your VBA instructions or in your Excel formulas. For example:
Sub Test() Dim x As Double ' Declares a variable of type Double x = 5 ' Assigns the value 5 to the variable MsgBox Square(x) ' Displays the square of x End SubOr
=SQUARE(A1) ' Calculates the square of the value in cell A1Conclusion
In this article, you learned how to use Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) in Excel. You saw what VBA is and why to use it, how to access VBA in Excel, how to write VBA code in Excel, how to use Excel worksheet functions in VBA, how to create macros in Excel with VBA, how to create forms in Excel with VBA, and how to create custom functions in Excel with VBA. Among the custom functions you can create with VBA is the function to perform subtraction in Excel . You can now leverage the programming power of VBA to customize and automate Excel to suit your needs.

![[GetPaidStock.com]-648864a469b9a](https://tt-hardware.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/GetPaidStock.com-648864a469b9a-696x400.jpg)


