Debian is a Linux distribution that stands out for its stability, security and modularity. It allows you to build your operating system in your own image, by choosing the applications that interest us, without any superfluities. In this comprehensive guide, we will explain how to install Debian 11 step by step, starting from a minimum version and configuring it according to your needs. Whether you are a beginner or an expert, you will find here all the information you need to successfully install Debian 11.
Here's an easy-to-follow video tutorial for installing Debian 11 !
How to download Debian 11?
To install Debian 11, you need an ISO file, which is a system image to burn to removable media (CD, DVD or USB stick). You can download this ISO file from the official Debian website or from a mirror. There are several types of ISO images:
- A minimal image (netinst): it contains only the basic utilities necessary to start the installation. It requires an Internet connection to download additional packages during installation. It is recommended if you want to customize your system as much as possible.
- A full image (DVD): it contains more packages and allows you to install the system without an Internet connection. It is recommended if you want to have a ready-to-use system with common applications.
- A live image: it allows you to test Debian without installing it on the hard drive. It contains a desktop environment and some applications. It also allows you to launch the installer from the live system.
You can choose the ISO image that matches your hardware architecture (64-bit or 32-bit) and your connection type (Ethernet or Wi-Fi). You can also choose between several desktop environments (GNOME, KDE, Xfce, LXDE…) if you opt for a full or live image.
Once you have downloaded the ISO image, you need to verify its integrity with the SHA-256 fingerprint of the original file. This allows you to ensure that the file is not corrupted or altered. You can use software like 7-Zip or HashTab on Windows , or the sha256sum command on Linux.
How to install Debian 11?
To install Debian 11, you must burn the ISO image to removable media (CD, DVD or USB stick) and boot your computer from this media. You can use software like Rufus or Etcher on Windows , or the dd command on Linux.

Once you boot to the installation media, you need to follow these steps:
- Choose the language, country and keyboard you want to use.
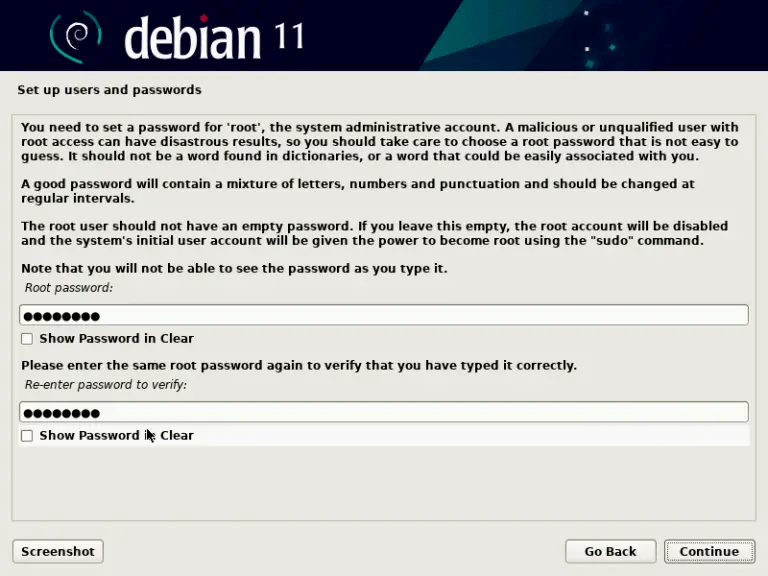
- Give your computer a name and choose a password for the root account, which is the system administrator.
Create a user account with a name and password.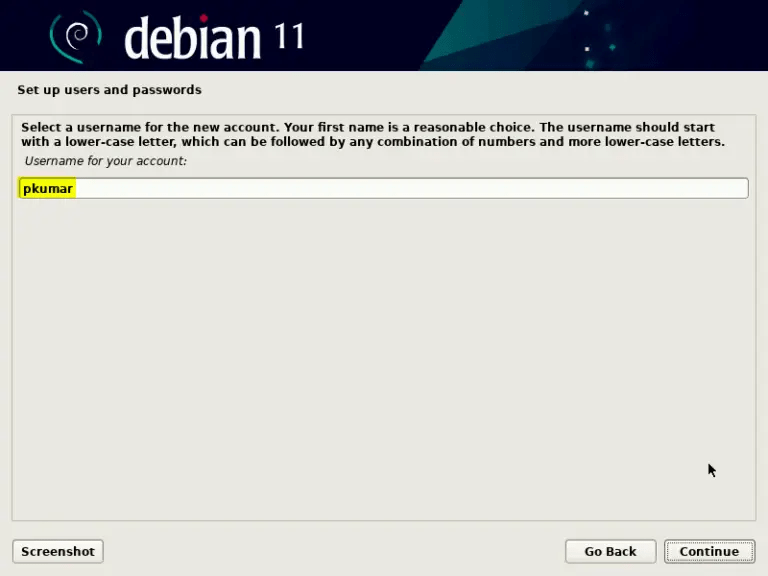
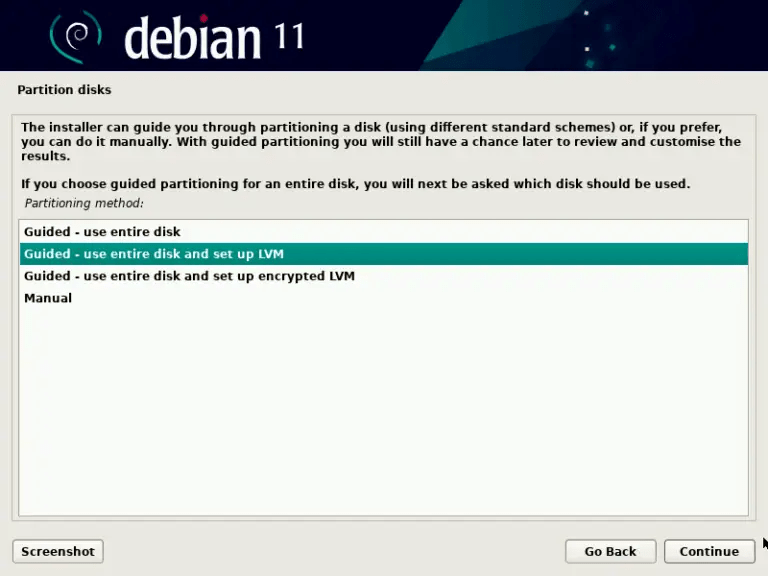
- Partition your hard drive as needed. You can choose between several options: use the entire disk, use the disk with LVM (Logical Volume Manager), use the disk with encrypted LVM, or partition manually. If you are unsure, choose the first option.
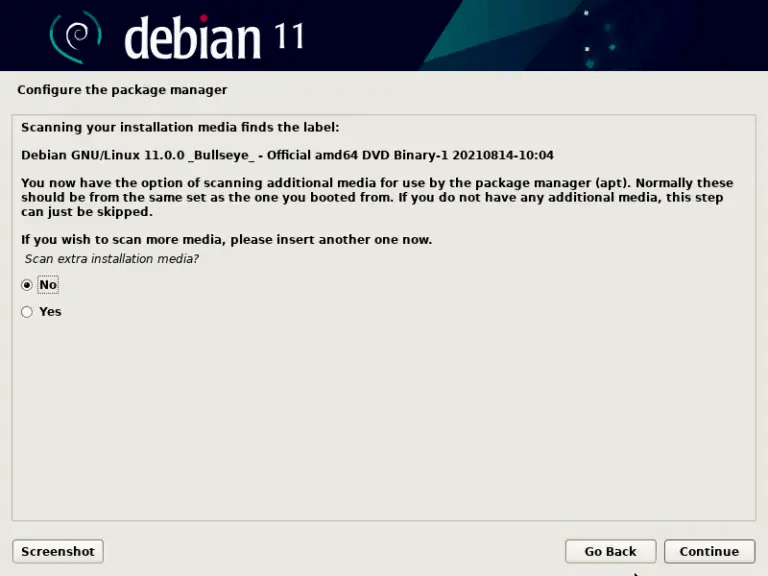
- Configure your package manager (apt) by choosing a download source (a Debian mirror or CD/DVD) and indicating whether you want to participate in the package popularity survey.
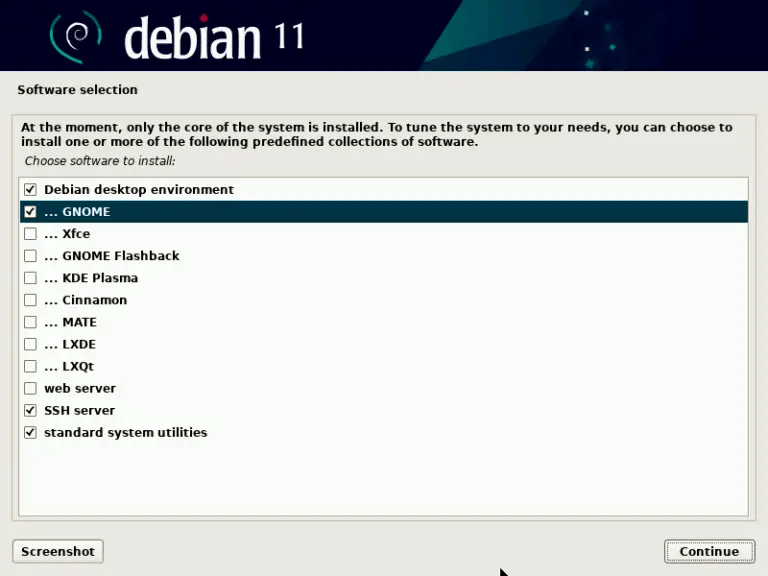
- Select the software you want to install. You can choose between several categories: desktop environment, web server, print server, file server, mail server, SSH server, common utilities. If you chose a minimal image, you can select nothing and install the software later.
- Install the boot loader (GRUB) to the boot sector of the hard drive. This will allow you to start Debian on the next reboot.
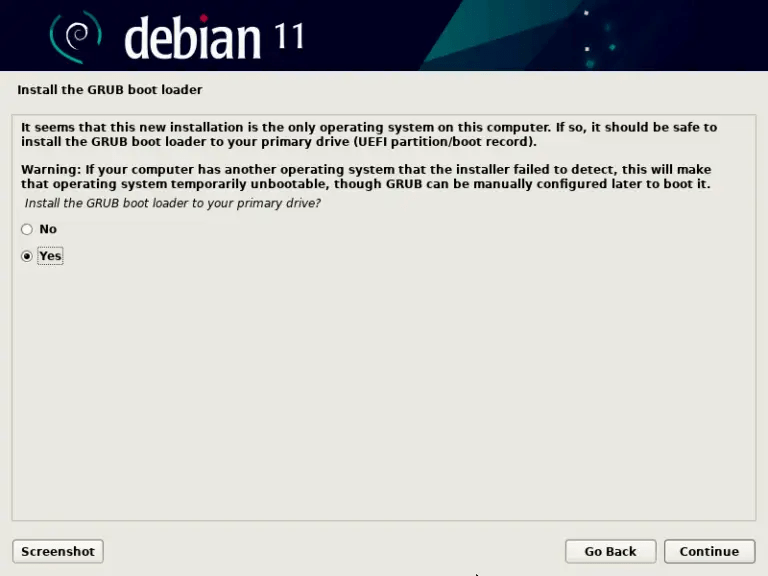
- Complete the installation and restart your computer.
Congratulations, you have installed Debian 11! You can now enjoy your new operating system.
How to configure Debian 11?
After installing Debian 11, you can configure it according to your preferences and needs. Here are some steps we recommend you follow:
- Check that your internet connection is stable and that you have no network problems. If you encounter the “Incomplete configuration due to limited connection” error, check out this article to resolve it .
- Edit the sources.list file (/etc/apt/sources.list) to point to the Debian 11 repositories. You can also add the contrib and non-free repositories if you want to access packages that do not respect totally the principles of free software. Here is an example of a sources.list file:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main contrib non-free deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main contrib non-free deb http://security.debian.org/debian -security bullseye-security main contrib non-free deb-src http://security.debian.org/debian-security bullseye-security main contrib non-free deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates main contrib non-free deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates main contrib non-free
- Update the system with the commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt full-upgrade
- Install the packages you are interested in with the command:
sudo apt install package-name
You can use the apt search command to search for a package by name or description.
- Set up a desktop environment if you don't already have one. You can choose between several options: GNOME, KDE, Xfce, LXDE, Cinnamon, MATE… For example, to install GNOME, use the command:
sudo apt install task-gnome-desktop
- Install sudo if you want to be able to run commands as root without having to enter the password every time. To do this, use the command:
su -c 'apt install sudo'
Then add your username to the sudo group with the command:
su -c 'adduser your-username sudo'
Log out and log back in for the changes to take effect.
- Install proprietary drivers for your NVIDIA graphics card if you have one. To do this, use the commands:
sudo apt install nvidia-driver sudo reboot
- Install Microsoft fonts if you want better compatibility with documents created under Windows . To do this, use the command:
sudo apt install ttf-mscorefonts-installer
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about Debian 11:
What is Debian?
Debian is a free operating system based on the Linux kernel. It has existed since 1993 and is developed by a community of volunteers. Debian aims to be a universal system, capable of running on different types of machines, from PCs to servers, including smartphones or connected objects. Debian is characterized by its social contract philosophy, which guarantees respect for the principles of free software, system quality and transparency of decisions.
Debian offers three different versions:
- Stable: the production version of Debian, which prioritizes security and stability. It contains tested and proven packages, but often old. This is the version recommended for professional or critical use.
- Testing: the intermediate version of Debian, which contains packages which have not yet been accepted in the stable version, but which are waiting to be accepted. It offers more recent versions of software, but may present bugs or incompatibilities. This is the version that prepares the release of the next stable version.
- Unstable: the continuously developing version of Debian, which receives the most recent software updates. It is intended for informed users who want to test new features or contribute to the project. It can be unstable or broken at any time.
How to change Debian version (stable, testing or unstable)?
To change the version of Debian, you must modify the sources.list file (/etc/apt/sources.list) and replace the code name of the current version (bullseye) with that of the desired version (buster for stable, bookworm for testing or sid for unstable). Then you must update the system with the commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt full-upgrade
Please note, this operation is irreversible. You cannot revert to an earlier version without reinstalling the system.
How to install software that is not in the official Debian repositories?
To install software that is not in the official Debian repositories, you have several options:
- Add third-party repositories to your sources.list file (/etc/apt/sources.list) if the software you want to install is available in a Debian-compatible repository. For example, to install Google Chrome, you can add the following repository:
deb [arch=amd64] http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main
Then you must import the repository key with the command:
wget -q -O - https://dl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo apt-key add -
Then you can install the software with the command:
sudo apt update sudo apt install google-chrome-stable
- Download the .deb file of the software you want to install from the developer's official website or from a third-party site. For example, to install Skype, you can download the .deb file from https://www.skype.com/fr/get-skype/. Then you can install the software with the command:
sudo dpkg -i filename.deb
- Compile the software from source if the developer provides the software source code. To do this, you need to download the source code archive from the developer's official website or from a third-party site. For example, to install GIMP, you can download the source code archive from https://www.gimp.org/downloads/. Then you must extract the archive with the command:
tar xvf archive-name.tar.gz
Then you must enter the extracted folder with the command:
cd folder-name
Then you must follow the instructions in the README or INSTALL file to compile and install the software. Generally, you must execute the following commands:
./configure make sudo make install
How to update Debian 11?
To update Debian 11, you need to run the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade sudo apt full-upgrade
The first command updates the list of packages available in the repositories. The second command updates installed packages that have a new version available. The third command updates installed packages that have a new version available and require other packages to be installed or removed.
How to uninstall Debian 11?
To uninstall Debian 11, you have several options:
- Reinstall another operating system on your hard drive by overwriting Debian 11. To do this, you need to boot to an installation media of the operating system you want to install and follow the instructions.
- Format your hard drive by deleting all partitions. To do this, you can use software like GParted or fdisk on Linux, or Diskpart on Windows .
- Keep Debian 11 and install another dual-boot operating system. To do this, you need to reduce the size of the Debian 11 partition with software like GParted or fdisk on Linux, or Diskpart on Windows . Then you need to create a new partition for the operating system you want to install. Then you need to boot to an installation media of the operating system you want to install and follow the instructions.




