RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a configuration of physical disks grouped into a single logical storage unit to improve data reliability and performance.
There are different RAID levels, used for redundancy, fault tolerance, and improved read/write performance. Fault tolerance provides data protection in the event of disk failure(s), depending on the RAID level chosen.
However, a RAID array is not immune to disk failures or data loss. Various causes, such as human error, hardware failures, software bugs, or firmware issues, can lead to such incidents.
Is it possible to recover lost data from a RAID?

In the event of data loss from a RAID, recovery depends on several factors: the RAID configuration, fault tolerance, the number of disks involved, the severity and type of loss, etc.
You can attempt to rebuild the RAID array to restore data access, but this requires precisely redefining parameters such as block size and order, disk offset, etc. An error in these settings or an interruption (power outage, system crash, etc.) during the rebuild can result in irretrievable data loss.
It is therefore imperative to adopt a well-thought-out strategy, adjusted to these different parameters, to carry out the recovery smoothly.
RAID Data Recovery Strategy
Recovering data from a failed RAID array without specialized tools or a methodical approach is strongly discouraged. Here is a three-step strategy for restoring an inaccessible or failed RAID array:
Part 1: Diagnosis
As soon as you notice the RAID failure, perform these checks:
- Stop all use of the RAID : any further operation could overwrite or permanently corrupt the data.
- Identify the cause of the failure : check for error messages in the RAID management software or in the BIOS (if configured at the BIOS level). A monitoring tool like CrystalDiskInfo can help detect hardware problems.
- Determine the RAID level : some levels (RAID 5, RAID 6) allow the loss of one or two disks without data loss, while others offer no tolerance. This information is crucial to determine if data recovery is possible.
- Prioritize your data : identify essential files (financial documents, identity documents, certificates) and target them first, before less critical files.
Part 2: Data Recovery
Once the diagnosis is complete, carefully follow these steps:
Step 1: Reconstruct the RAID array
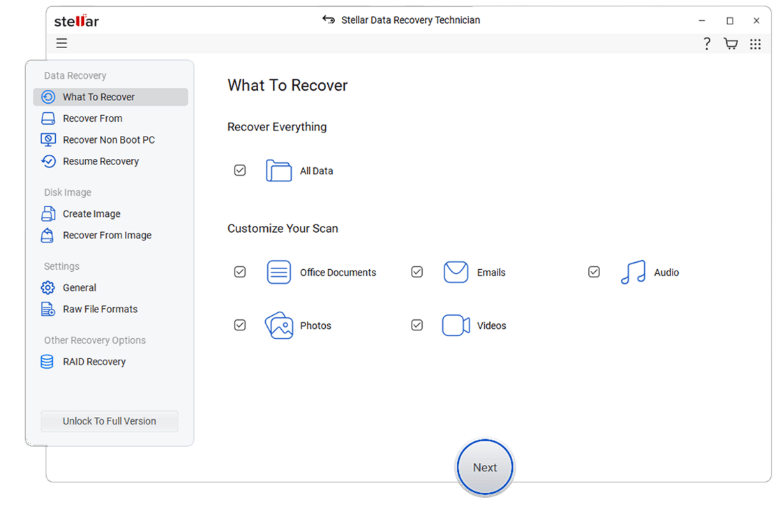
Use disk imaging software or a RAID recovery tool to create a virtual image of the array. Some tools automatically detect RAID settings, reducing the risk of errors. The virtual image allows you to operate without directly accessing the disks, thus protecting them from stress or damage.
Step 2: Scan the RAID image
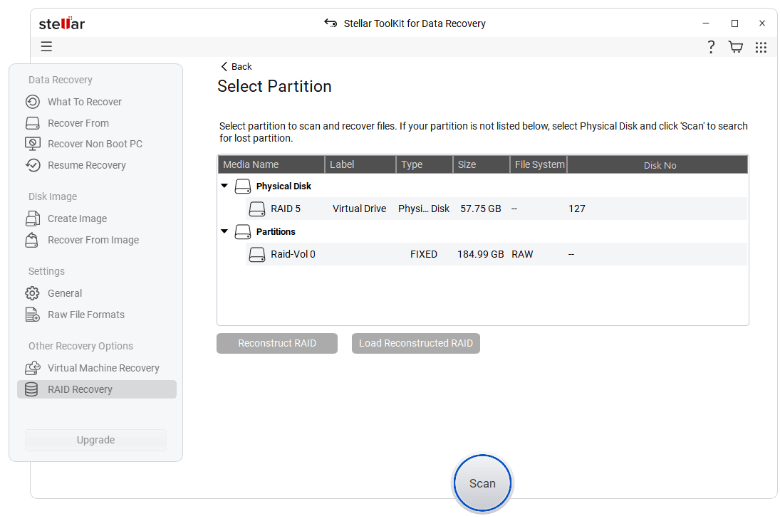
Analyze the image using reliable RAID recovery software. A deep, byte-level scan can reveal recoverable data that would otherwise go undetected.
Step 3: Verify data integrity
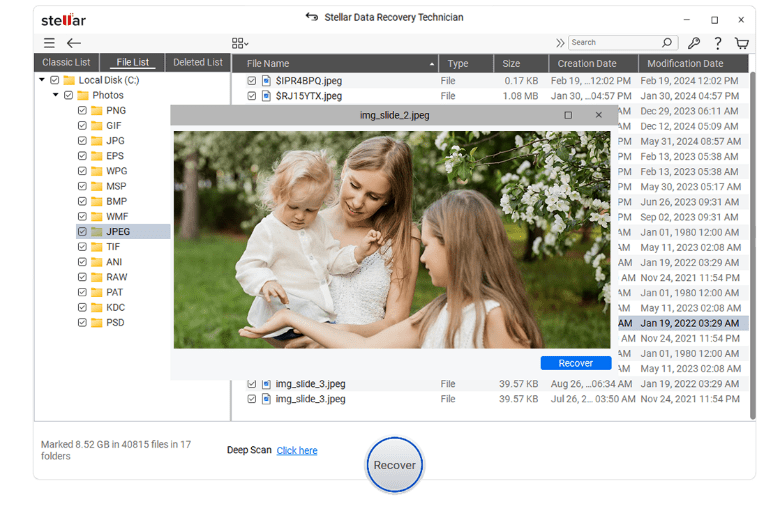
Preview the recoverable files before starting the recovery process to verify that they are intact.
Step 4: Start the recovery
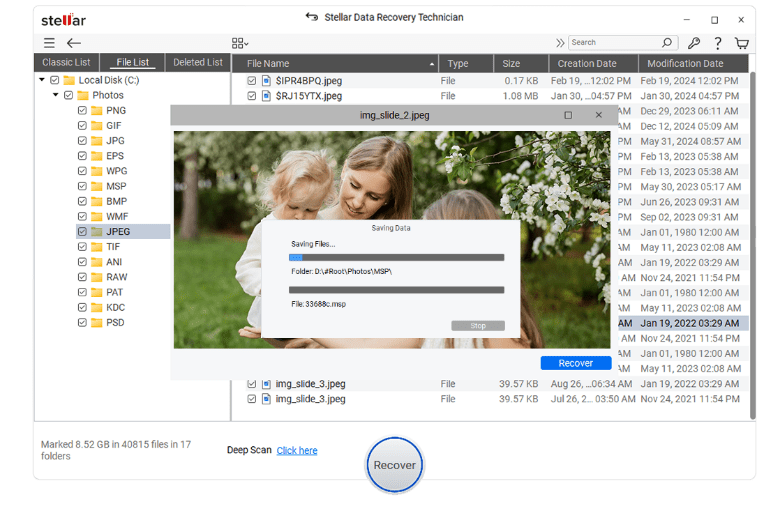
Once you have checked for recoverable files, use RAID recovery software to retrieve the data. It is advisable to back up the recovered data to another location, such as an external storage drive with sufficient storage capacity.
To recover data from a RAID array, you can use a reliable RAID data recovery tool, such as Stellar Data Recovery Technician. This is advanced RAID recovery software that allows you to perform the processes mentioned in the steps above.
You can use it to create a virtual image of the RAID array and analyze it to perform RAID data recovery. It also features a built-in drive monitor that you can use to check the status of member drives. In short, it's a comprehensive software solution that simplifies RAID data recovery.
You can use this software on a system operating under Windows 8, 8.1, 10 or 11 to recover data from RAID 0, 5 or 6, in a few simple steps.
Part 3: RAID Restoration
Once the data has been retrieved:
- Address the root cause of the failure (replace faulty disks, update firmware, change RAID controller, etc.).
- Rebuild the RAID array once the problems are resolved.
Tips to prevent RAID failures and avoid data loss
- Regularly monitor the condition of the disks and immediately replace any unit showing signs of failure.
- Prepare a hot-swap replacement disk to minimize downtime and facilitate rebuilding.
- Do not consider RAID as a backup solution : apply the 3-2-1 strategy (3 copies, 2 different media, 1 off-site).
- Ensure the environment is well ventilated and clean.
Conclusion
Various reasons, such as the failure of a member disk, the loss of a partition, etc., can lead to data loss from a RAID array. Recovering data from a RAID array is a complex task as it requires expertise in RAID manipulation. You can simplify the RAID recovery process by using RAID data recovery software .




